If you’ve lost your job through no fault of your own, we’re here to help. This page outlines your rights and responsibilities while filing for benefits, helping you avoid potential issues or delays.
Once you file your claim, you’re responsible for meeting Virginia’s unemployment benefit requirements.
What is Unemployment Insurance?
The intent of Unemployment Insurance is to pay benefits to workers during times of unemployment when suitable work is not available. These benefits are funded through taxes paid by employers covered under the Virginia Unemployment Compensation Act. No part of the cost of your unemployment benefits is deducted from your earnings.
Your Potential Entitlement
After filing your initial claim for unemployment benefits, you’ll receive a Statement of Wages and Potential Entitlement. This document outlines your potential weekly benefit amount and the number of weeks you may receive benefits, if you qualify. These figures are calculated based on your earnings from covered employment during the Base Period.
It is crucial that you read this statement carefully to ensure all your employers and wages have been reported correctly.
The Base Period helps determine your benefit eligibility. Here’s how it works:
- The Base Period consists of the first four of the last five completed calendar quarters before your claim’s effective date
- Your claim’s effective date is always the Sunday of the week you file
If you don’t qualify for benefits under this Regular Base Period, you may still qualify under an Alternate Base Period. However, please note you cannot choose which Base Period applies to your claim.
Base Period Calculator
This online tool can help you quickly and accurately identify your personal base period.
Regular Base Period
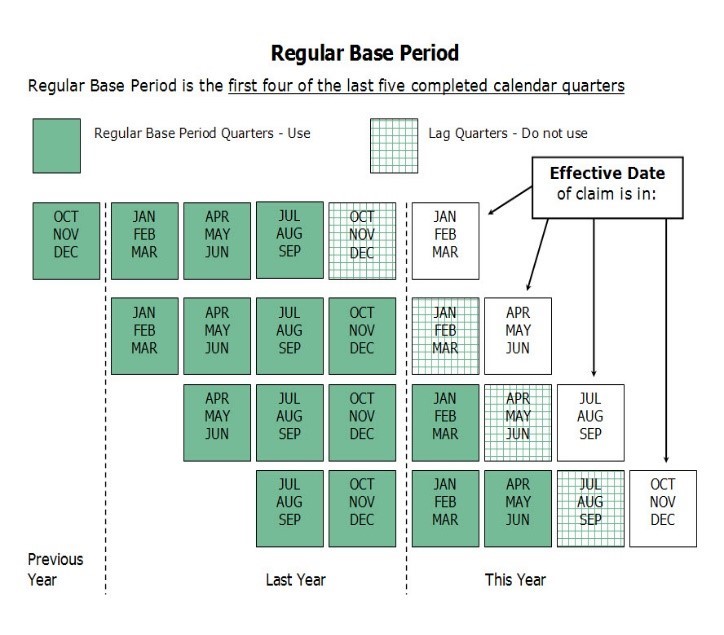
Visualization of the Regular Base Period.
Alternative Base Period
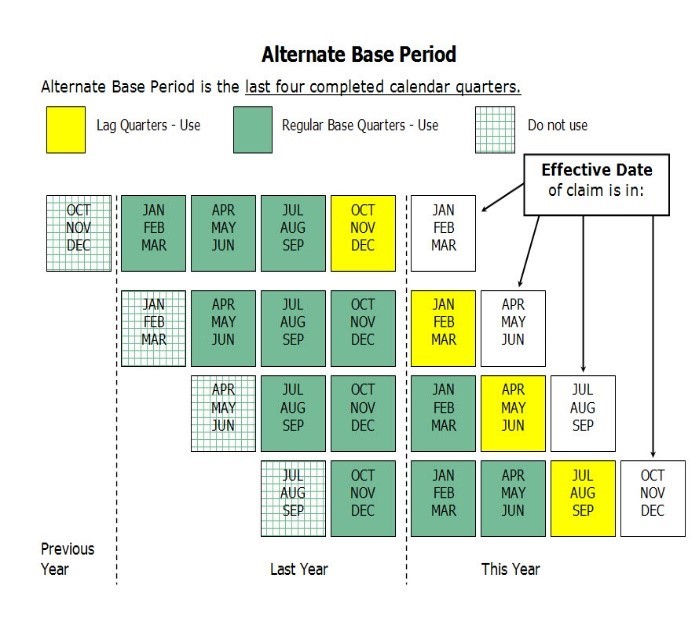
Visualization of the Alternative Base Period.
The weekly benefit amount (WBA) depends on when your claim becomes effective and your wages earned during the Base Period.
For claims filed before January 4, 2026:
The maximum weekly benefit amount is $378 and the minimum is $60.
For new claims filed on or after January 4, 2026:
The maximum weekly benefit amount increases to $430, while the minimum increases to $112.
To qualify for the maximum weekly benefit amount, your combined earnings from two quarters in the Base Period must total at least $18,900.01.
For more information, please review the benefit table: bentable.pdf.
You must report all gross wages, not net wages, during the week they are earned, not paid. If the gross wages, not net wages, you earn are less than your weekly benefit amount, you may receive unemployment benefits. However, the amount of gross wages that are more than $100 will be deducted from your weekly benefit amount. If your gross weekly wages are equal to or more than your weekly benefit amount, you will not be paid benefits for that week.
For example, if your gross weekly wages are $200 and your weekly benefit amount is $300, your reduced benefit amount is $200. We calculate this by:
- Subtracting the $100 from the gross wage: $200 - $100 = $100
- Subtracting the calculated amount from the benefit amount: $300 - $100 = $200
To receive benefits, you must have earned at least $3,000 in your two highest paying quarters combined.
Your Weekly Benefit Amount (WBA) is based on your wages from your two highest quarters, up to Virginia's legal limit.
Your Maximum Benefit Amount (MBA) is the maximum you can receive during your benefit year. It’s based on your total Base Period wages, which are also subject to the state's legal limit.
| Effective Date of Claim | Base Period | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Year | Previous Year | Last Year | This Year | ||||
| January February March | |||||||
| October November December | January February March | April May June | July August September | ||||
| April May June | |||||||
| January February March | April May June | July August September | October November December | ||||
| July August September | |||||||
| April May June | July August September | October November December | January February March | ||||
| October November December | |||||||
| July August September | October November December | January February March | April May June | ||||
Estimate Your Benefits
Use ID.me to log in to the Customer Self Service (CSS) system to estimate your weekly unemployment insurance benefits.
To be eligible to receive unemployment benefits, you must be able and available to start work immediately, and actively seek suitable employment.
- You must make work search contacts within the week you’re claiming your benefits.
- You must contact at least two different employers each week.
- Job contacts cannot be repeated with the same employer unless you are applying for different job openings with that employer.
- All work search contacts are subject to verification. Your claim may be selected for an audit.
- You must report all work performed and wages earned each week. This includes self-employment and gig work such as food delivery and ride sharing services.
- You must submit job contacts to the VEC. If you file online, submit through Customer Self Service. Telephone filers will submit basic information by phone, then detailed written information every four weeks using the Work Search Record form we provide you.
- While you may prefer telework, you must be ready and able to accept non-remote work.
The amount of unemployment that you are eligible for is based on the wages earned through covered employment during your Base Period. Covered employment is work performed for an employer who is subject to the Virginia unemployment tax laws. Work performed for an employer who is not subject to these laws cannot be used on your claim.
For example, work performed for some religious and nonprofit organizations, commissions earned as a real estate agent or insurance agent, and wages earned as elected government officials is not covered employment.
Yes. These wages may be used if they were subject to unemployment tax, were earned in the Base Period, have not been used to establish a previous unemployment claim, and are in accordance with other unemployment compensation laws.
Yes. Unemployment benefits are subject to federal income tax and must be reported as income when you file your taxes.
By January 31st of each year, the VEC will send you a form 1099-G with the amount of unemployment benefits you received the prior year. If you have a change of address, notify the VEC by December 27th to ensure proper delivery of your 1099-G. Your 1099-G will be mailed to your address on file and will NOT be forwarded.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION ABOUT WAGE STATEMENT ACCURACY
If the wages on your Statement of Wages and Potential Entitlement are listed incorrectly or are missing, or if there are employers listed that you did not work for, follow the instructions on your Statement for submitting proof of missing wages.
Denial of Benefits
You may be monetarily eligible for unemployment benefits and still be denied benefits for other reasons. Any situation that may keep you from receiving benefits is called an ISSUE.
If there is an issue, we may ask you to provide information concerning your separation, your ability to work, or any activities or conditions which could keep you from seeking or accepting work.
Quick Tip
We may need to contact you for more information about your claim, so remember to check your mail often and always keep your mailing address up to date. Most correspondence can be reviewed digitally, and your contact information can be updated in the Customer Self Service portal.
If you fail to respond to a request for information, we may have to deny your benefits.
You might not get benefits if you:
- Were fired, suspended, or let go from your last job because of misconduct
- Voluntarily quit your last job without good cause and without pursuing all reasonable alternatives with the employer prior to quitting
- Are not able or available to look for and accept work
- Fail to search for or accept work
- Refuse a job offer or referral for suitable work
- Fail to take part in Reemployment Services
- Have set limits on the type of work, wages, hours, days, or locations you’ll accept.
- Work full-time
- Are a union member involved in a strike
- Are self-employed
- Worked for an educational institution (under certain conditions)
- Receive a pension, retirement pay, or annuity
- Receive severance, vacation, holiday, or other types of pay
- Are receiving Workers’ Compensation
- Are not a U.S. citizen and don’t have authorization to work in the U.S.
Failure to Use Reemployment Services
Local Workforce Centers provide job search and placement services such as counseling, assessments, job search workshops, and employer referrals. Using federal guidelines, we screen all unemployment claims to identify those who might benefit most from these reemployment services.
If you’re selected for a reemployment program and cannot attend, you must contact the local Workforce Center to reschedule. Failure to participate will result in loss of benefits.
Refusing a Job Offer or VEC Referral
If you refuse a job offer, the VEC will ask you for more information. We will then decide if the work was suitable and if you had good reason to refuse it.
If you refuse or fail to apply for suitable work without good cause, your benefits may be denied starting from the Sunday of the week when the refusal occurred.
Reporting Work and Income While Receiving Benefits
You must report any work, including full-time, part-time, temporary jobs, short-term contracts, volunteer work, training, or cash jobs like mowing lawns or babysitting, when filing for unemployment. Work includes anything you do for pay during the week you're claiming benefits.
You must report all gross earnings before taxes, even if you haven't been paid yet. If you don’t report all earnings, it can lead to overpayment and may be considered fraud.
You also must report income from other sources, such as retirement, pensions, disability, self-employment, or education and training allowances. All income from any source must be reported.
If you obtain full-time employment, stop filing for benefits.
Reporting Pension, Retirement Pay, and Annuities
Pension, retirement pay, annuities, or similar payments (like a 401K) from past work may reduce your weekly unemployment benefits or disqualify you. You must inform the VEC if you're receiving, have applied for, or if there are any changes in these payments.
Your weekly benefits will be reduced by the full amount of your pension. If you get a lump sum from a retirement plan, it may be deducted in the week you receive it.
Reporting Severance, Vacation, Holiday, and Other Pay
You must report severance pay, vacation pay, holiday pay, and similar payments like bonuses or pay instead of notice. These may reduce your weekly unemployment benefits.
If you're applying for or receiving Workers' Compensation, you will need to provide a medical statement about your ability to work.
Distribution of Child Support Withholding
The Division of Child Support Enforcement (DCSE) will notify the VEC of any child support withholdings. If you do not agree with the amount, you must contact the DCSE, since the VEC cannot remove or reduce the amount of the distribution.
Distribution of Federal Tax Withholding
If you chose to have federal taxes withheld from your weekly unemployment benefits, the VEC will send your withholding amount to the IRS as each payment is processed.
Distribution of Overpayment
Benefits will not be paid on a regular unemployment insurance claim until any outstanding overpayment has been recovered. To recover the overpayment, the VEC may deduct it from your current or future benefit payments.
Benefit Overpayment
An overpayment happens when you receive unemployment benefits that you weren't supposed to get. This can include money paid while your former employer's appeal was being reviewed, or if you didn't tell us information that could have changed or stopped your benefits.
Being overpaid for some benefits does not mean that you were never entitled to benefits previously, or that you will not be eligible in the future.
Overpayments are discovered a variety of ways, including:
- New hire information received from employers
- Audits
- Tips received from the State Fraud Hotline
If you receive benefits to which you are not entitled, you will be liable for repayment of those benefits along with any costs, fees, and interest associated with collection. If someone else made the mistake that caused the incorrect payment, you will still be liable for repayment.
- Failing to correctly report your gross amount of earnings before deductions or deductible income.
- Continuing to receive unemployment benefits after returning to work. You must report your gross earnings in the week you earned them, NOT the week you receive your payment.
- Failing to report ALL gross earnings from work while claiming benefits.
- Failing to provide information that could affect your claim.
- Receiving benefits that you are later disqualified from.
Yes. When an overpayment is established, you will receive a written decision explaining why you are being overpaid. If you disagree with the reason you are being overpaid, you have 30 days from the date the decision is issued to file an appeal. If you do not believe you have grounds for an appeal, you may be eligible to apply for a Waiver of Repayment that will allow you to avoid paying back the overpayment.
Apply for a Waiver of Repayment
If you were overpaid benefits and qualify for a waiver, we’ll mail you a waiver application. You can view any correspondences through Customer Self Service. You can waive the repayment if the overpayment was not your fault and the loss of that income would cause you serious financial trouble.
You must repay an overpayment by mail. Follow the instructions printed on the letter you received. You can repay in one lump sum or under an installment payment plan. If you are unable to repay the full amount in one payment, you must immediately contact the Benefit Payment Control Unit at (804) 786-8593 to arrange a repayment installment plan.
If you don’t repay the overpayment in full, the VEC may use other methods to collect the money owed, including:
- State income tax refund intercept
- Federal income tax refund intercept
- Collection agency
- Bankruptcy proceedings
- State agency payment intercept (ex. lottery winnings)
- Deduction from current unemployment benefits
We cannot pay benefits on an unemployment insurance claim until we’ve recovered outstanding overpayment(s).
Appeals
We will mail you our decision on your benefits, explaining why they were approved or denied. If you do not understand the decision, contact us at (866) 832-2363.
If you do not agree with the decision, you have 30 days from the date the decision is issued to file an appeal. Other interested parties, such as your employer(s), may also appeal the same decision. The appeal must be in writing and should explain the reasons it is being sought. If an appeal is filed, you should continue to file your weekly claim each week.
File an Appeal
- You must continue to file your weekly claim during the appeal process to protect your rights to benefits.
- Be aware that employers have the same appeal rights.
- If the appeals decision denies your benefits, any payments you’ve already received will be considered overpaid.
- It is important that you participate in the hearing on the employer’s appeal so you may present your side of the case.
Fraud and Misrepresentation
In the context of unemployment insurance, fraud is knowingly making a false statement, misrepresenting a material fact, or withholding information to obtain unemployment benefits. Any information you provide to get unemployment benefits will be checked. If fraud is found, you’ll have to pay back the benefits. You could also face criminal charges, fines, or even jail time.
The VEC is responsible for protecting the Unemployment Insurance Trust Fund, which is used to pay unemployment benefits to those who qualify. The VEC has a full-time fraud detection unit to identify and recommend criminal prosecution for those who commit fraud.
- Failure to properly report a job separation
- Failure to properly report gross earnings
- Failure to disclose that you are not able and available for work
- Failure to report all gross earnings from any source
- Divulging your Personal Information Number (PIN) to anyone
- Allowing another person to file your weekly claim
- You won’t be able to receive unemployment benefits for 52 weeks
- You’ll have to repay the benefits you got through fraud, plus an extra 15% penalty
- You could face criminal charges under federal or state law
- You could be sent to prison

